BAQA’s Piercing Standards are designed to unify a wide range of regional regulations and industry best practices into a comprehensive global benchmark. By ensuring safe, hygienic, and professional piercing procedures, we help protect clients and empower piercing specialists worldwide.

1. Introduction & Scope
Body piercing has been practiced across various cultures for centuries. It involves creating an opening in the body to insert jewelry or ornaments. To maintain high levels of client safety and professional integrity, BAQA’s standards cover:
- Health & Safety Protocols: Requirements for sterilization, PPE, and contamination control.
- Equipment & Jewelry Guidelines: Specifications for approved materials, jewelry sizes, and maintenance procedures.
- Anatomical Knowledge & Technique: Best practices for evaluating piercing sites and performing procedures with precision and care.
- Ethical & Professional Conduct: Policies on informed consent, client communication, and responsible practice.
These standards apply to all BAQA-accredited piercing artists, studios, and training centers. They also serve as a valuable reference for anyone aiming to meet the highest global benchmarks in body piercing.
2. Health & Safety Protocols
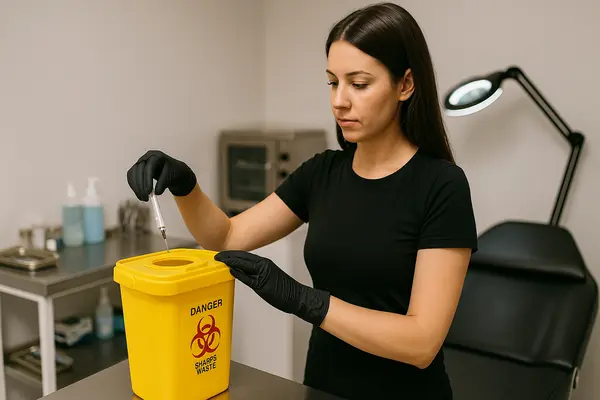

2.1 Sterilization & Disinfection
- Tools & Instruments: Use single-use, pre-sterilized needles for each piercing. Instruments like forceps or clamps should be sterilized in a Class B autoclave or equivalent medical-grade sterilization equipment.
- Surface Disinfection: Clean work surfaces thoroughly with approved disinfectants before and after each piercing session.
- Disposable Barriers: Use disposable covers for chairs, trays, and light fixtures to minimize cross-contamination.
2.2 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Gloves: Always wear single-use, medical-grade gloves. Discard and replace gloves if contamination is suspected or if you leave the sterile field.
- Masks & Protective Clothing: Wear masks, protective eyewear, or gowns as needed when there is a risk of bodily fluid contact.
- Client Protection: Provide disposable bibs, drapes, or coverings to maintain a clean environment and client comfort.
2.3 Cross-Contamination Prevention
- Hand Hygiene: Thoroughly wash and disinfect hands before donning gloves, as well as immediately after glove removal.
- Sharps Disposal: Dispose of needles in designated sharps containers per local biomedical waste regulations.
- Instrument Handling: Use separate trays or containers for clean and used instruments to prevent mix-ups.
3. Equipment & Jewelry Standards

3.1 Approved Jewelry Materials
- Hypoallergenic Metals: Use implant-grade titanium, surgical stainless steel, niobium, or gold (14k or higher) to reduce risks of allergic reactions.
- Quality Assurance: Confirm that all jewelry meets international or local standards (e.g., ASTM F136 for titanium or ASTM F138 for steel).
- Surface Finish: Jewelry must be free from scratches or sharp edges that could irritate tissue or harbor bacteria.
3.2 Size & Gauge Selection
- Appropriate Gauge: Base gauge selection on the piercing location and client anatomy. Using the correct gauge can aid in proper healing and minimize complications.
- Length & Diameter: Ensure the post or ring diameter is sufficient to accommodate any swelling during the initial healing phase.
3.3 Maintenance & Storage
- Clean Storage: Keep all jewelry organized in clean, labeled containers to maintain sterility and prevent damage.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect tools and jewelry for defects, corrosion, or contamination.
4. Anatomical Knowledge & Technique
4.1 Site Assessment
- Anatomical Variation: Recognize differences in clients’ anatomy to determine the most suitable piercing site and approach.
- Contraindications: Assess for skin conditions, scarring, or medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, blood disorders) that may affect healing.
4.2 Piercing Methods
- Marking & Alignment: Mark piercing sites with skin-friendly pens to ensure accurate placement. Confirm alignment and aesthetics with the client before proceeding.
- Needle Insertion Technique: Practice safe, swift, and controlled needle insertion, minimizing tissue trauma.
- Jewelry Insertion: Insert jewelry immediately, ensuring a sterile environment and smooth transition to reduce discomfort.
4.3 Pain Management & Comfort
- Client Consultation: Discuss pain levels, possible anxieties, and methods to reduce discomfort (e.g., deep-breathing techniques).
- Topical Anesthetics (if permitted): Use only approved products and obtain informed consent. Follow local regulations regarding anesthetic use.
5. Client Consultation & Consent

5.1 Pre-Piercing Consultation
- Medical Disclosure: Request relevant medical history, including allergies, medications, and recent surgeries.
- Procedure Explanation: Describe the steps of the piercing, potential risks, and estimated healing timelines.
- Design & Placement: Collaborate with the client on jewelry selection and placement based on their style, anatomy, and healing considerations.
5.2 Consent Forms
- Legal Age Requirements: Strictly adhere to local age restrictions and verification procedures.
- Informed Consent: Provide written documentation explaining the procedure, potential complications, and client responsibilities for aftercare.
- Privacy & Data Handling: Safeguard personal client information and comply with relevant data protection laws.
6. Aftercare & Healing

6.1 Immediate Aftercare
- Initial Dressing: Provide a sterile covering if necessary (depending on location and local practices).
- Cleaning Protocol: Offer detailed instructions on cleaning the piercing site (e.g., saline solutions), frequency of cleaning, and products to avoid.
- Lifestyle Considerations: Advise clients on activities that could impact healing (e.g., sports, swimming, wearing certain types of clothing).
6.2 Ongoing Healing Support
- Check-Ups: Encourage follow-up visits or calls to assess the healing progress and adjust jewelry if needed.
- Warning Signs: Inform clients about symptoms of infection or rejection (e.g., prolonged redness, discharge, severe swelling).
- Jewelry Change: Advise clients on when and how to safely change jewelry post-healing, or recommend professional assistance.
7. Ethical & Professional Conduct

7.1 Client Respect & Confidentiality
- Professional Communication: Always address client concerns respectfully and maintain a calm, courteous demeanor.
- Privacy: Offer discreet and comfortable spaces for piercings that involve sensitive areas.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect cultural or religious beliefs that might influence a client’s piercing preferences.
7.2 Professional Development & Community
- Continued Education: Stay updated on emerging techniques, tools, and regulations through BAQA-accredited courses and seminars.
- Collaboration: Share knowledge and best practices with peers to foster a safer, more informed industry.
- Mentorship: Experienced piercers are encouraged to mentor apprentices, helping standardize high-quality practices.
8. Compliance & Audits
Practitioners and studios registered with BAQA may be subject to periodic compliance reviews or audits:
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of sterilization processes, client consent forms, and daily checklists.
- Random Inspections: BAQA or local health authorities may conduct unscheduled inspections to ensure continuous adherence to safety standards.
- Non-Compliance Actions: Violations of BAQA standards can result in corrective measures, penalties, or accreditation revocation.
9. Ongoing Updates & Best Practices
Because the piercing industry evolves through new techniques, technology, and research, BAQA regularly updates its standards. Accredited members receive notifications and resources to help them stay aligned with the latest best practices.
Conclusion
By following BAQA’s Piercing Standards, practitioners demonstrate a commitment to protecting clients, refining their craft, and upholding the highest ethical and professional values. We invite piercers worldwide to join us in creating a consistent, globally recognized standard that both artists and clients can trust.
“Through dedicated adherence to safety, skill, and ethical conduct, the piercing industry can flourish across borders and cultures.”
— BAQA Standards Committee
